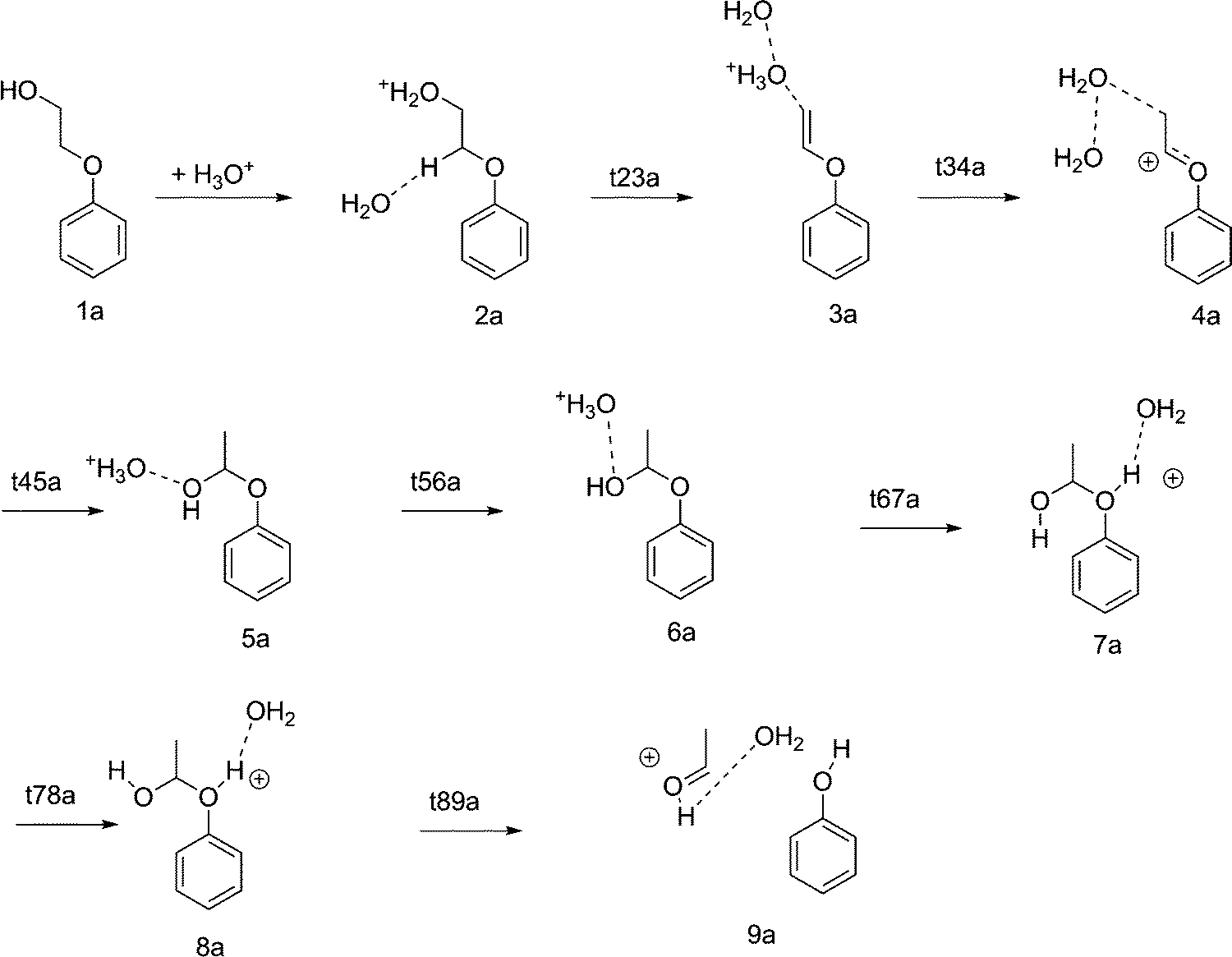
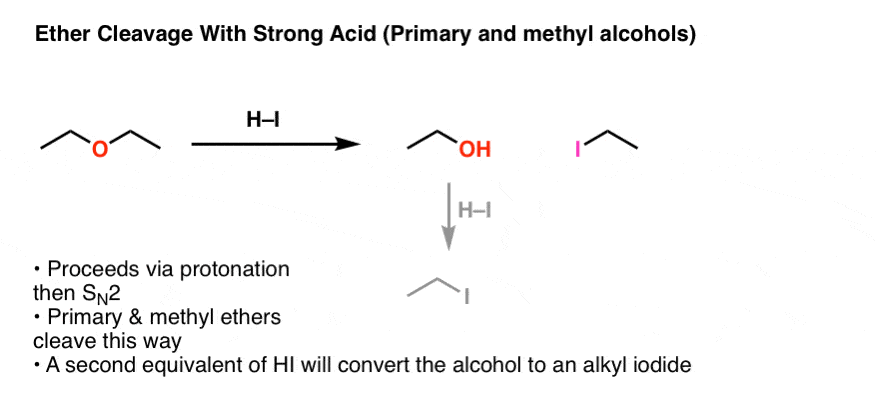
Hydrolysis Of Vinyl Ether Mechanism

Direct synthesis of cyclic ketals of acetophenones by palladium catalyzed arylation of hydroxyalkyl vinyl ethers.
Hydrolysis of vinyl ether mechanism. The reaction is first order in ethyl vinyl ether and first order in hy. The facile general acid catalyzed conversion of 2 ethoxy 1 cyclopentene 1 carboxylic acid to cyclopentanone. Vinyl mathrm sp 2 cations are very unstable and an mathrm s n1 type dissociation of meoh is very unlikely. Chemistry of heterocyclic compounds 1986 22 10.
Chem 2013 78 9815 9821. Ester hydrolysis reaction mechanism. Synthesis and mechanism of acidic hydrolysis of cis and trans 10 2 phenylvinyl phenothiazines. Identify allyl vinyl.
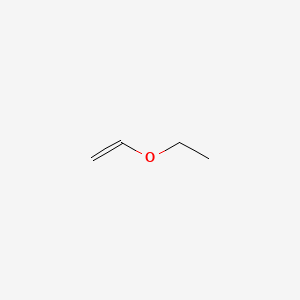
Methyl vinyl ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula ch 3 och ch 2 a colorless gas it is the simplest enol ether it is used as a synthetic building block as is the related compound ethyl vinyl ether a liquid at room temperature. Furthermore the reaction enables a facile entry to labile diarylacetaldehydes by tfa mediated hydrolysis of the β β disubstituted vinyl ethers. In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The kinetics of the acid catalysed hydrolysis of ethyl vinyl ether in aqueous solution have been measured by following the disappearance of the ether and by following the appearance of acetaldehyde.
Rates of hydrolysis of cis and trans β phenylvinyl methyl ethers cis and trans β p nitrophenyl vinyl methyl ethers and cis and trans β cyanovinyl ethyl ethers were measured in concentrated 10 55 wt aqueous perchloric acids the results show that these cis and trans isomers do not interconvert under the hydrolysis reaction conditions and that formation of the alkoxy carbonium ion. A number of functional groups are well tolerated under the reaction conditions. The journal of organic chemistry 1997 62 22. Xx with permission from the centre national de la recherche scientifique cnrs and the royal society of chemistry.
The general structure is r 2 c cr or where r h alkyl or aryl a common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers with the formula roch ch 2 important enol ethers include the reagent 3 4 dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether. The two methods give identical rate constants. For reproduction of material from njc.