Hydrolysis Of Vinyl Ethers

The yields were 94 for both temperatures.
Hydrolysis of vinyl ethers. Direct synthesis of cyclic ketals of acetophenones by palladium catalyzed arylation of hydroxyalkyl vinyl ethers. Vinyl mathrm sp 2 cations are very unstable and an mathrm s n1 type dissociation of meoh is very unlikely. They will make you physics. In the example the oxygen atom in methyl tert butyl ether is reversibly protonated.
8 21 227 228 the mechanism for chain transfer is shown in scheme 9 for the case of α benzyloxystyrene 15 the driving force for fragmentation is provided by formation of a strong carbonyl double bond. Jee main pattern questions exercise 1 misostudy duration. It is also important that r is a good radical leaving group. The kinetics of the acid catalysed hydrolysis of ethyl vinyl ether in aqueous solution have been measured by following the disappearance of the ether and by following the appearance of acetaldehyde.
It is nucleophilic on the α carbon and you can protonate it on that carbon almost like you are tautomerising an enol back to a ketone. Mole concept some basic concepts of chemistry. The reaction is first order in ethyl vinyl ether and first order in hy. Secondary deuterium isotope effects on the hydronium ion catalyzed hydrolysis of acetaldehyde diethyl acetal and ethyl vinyl ether were determined in wholly aqueous and aqueous dioxane solutions by comparing rates of reaction of the normal substrates with those of cd sub 3 ch oc sub 2 h sub 5 and ch sub 3 cd oc sub 2 h sub 5 and of cd sub 2 choc sub 2 h sub 5 and ch sub 2 cdoc sub 2 h.
Lectures by walter lewin. Vinyl ethers 1 x ch 2 a o can be very effective addition fragmentation chain transfer agents. The vinyl diethylisopropylsilyl ether monomer was polymerized at 0 and 25 c by the indticl 3 catalyst. The reaction was very fast under these conditions since the solution in the early minutes had a high viscosity due to the activity of the catalytic system in the polymerization.
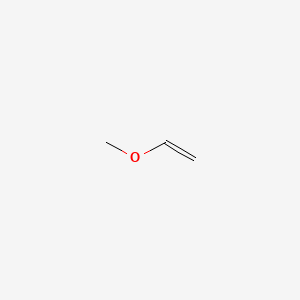
In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The unimolecular s n 1 mechanism proceeds via a carbocation provided that the carbocation can be adequately stabilized. The general structure is r 2 c cr or where r h alkyl or aryl a common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers with the formula roch ch 2 important enol ethers include the reagent 3 4 dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether. For the love of physics walter lewin may 16 2011 duration.
S n 1 ether cleavage. The resulting oxonium ion then decomposes into methanol and a relatively stable tert butyl cation the latter is then attacked by a nucleophile halide here bromide. The two methods give identical rate constants.